The Role of P2 Receptor-Mediated Component in Neurogenic Tone Control of Human Great Saphenous Vein
The aim of the investigation was to evaluate experimentally the role of the P2 receptor-mediated component in neurogenic tone control of human varicose-affected and healthy great saphenous vein (GSV).
Materials and Methods. The material for the study were segments of GSV obtained from two groups of patients: group 1 (n=14) included patients with varicose vein disease, in whom GSV was removed during surgical treatment; group 2 (n=21) comprised patients with coronary artery disease who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting using GSV as an autograft. Mechanical activity of the isolated veins was studied in vitro by electrical stimulation before and after incubation with atropine and phentolamine, pyridoxal-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2’,4’-disulfonate (PPADS) and suramin (both nonselective antagonists of P2 receptors), and also after desensitization of P2X receptors by α,β-methylene ATP.
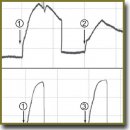
Results. Atropine and phentolamine did not completely inhibit the contractile responses evoked by electric field stimulation of the varicose and non-varicose GSV. PPADS (10 and 30 μМ) and suramin (100 and 300 μМ) significantly reduced the contractile amplitude of GSV response in both groups of veins (p<0.05) in the presence of atropine and phentolamine. α,β-methylene ATP (10 μМ) did not significantly reduce the amplitude of the GSV contractile response (p>0.05). Atropine, phentolamine and PPADS inhibited the contractile responses to a lesser extent in the varicose-affected veins compared to the veins unaffected by varicose disease.
Conclusion. These experimental results suggest the presence of the P2 receptor-mediated component in the neurogenic control of human GSV tone. Further studies of the P2 receptor mechanism of action is promising for the development of drugs both for treating varicose veins and for preventing spasm of the venous grafts after aortocoronary bypass surgery.
- Burnstock G., Ralevic V. Purinergic signaling and blood vessels in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 2014; 66(1): 102–192, https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.113.008029.
- Ziganshin A.U., Ziganshina L.E. P2-receptory: perspektivnaya mishen’ dlya buduschikh lekarstv [P2 receptors: perspective targets for future drugs]. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media; 2009.
- Burnstock G. Purine and pyrimidine receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 2007; 64(12): 1471–1483, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-6497-0.
- Burnstock G. Purinergic regulation of vascular tone and remodelling. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol 2009; 29(3): 63–72, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-8673.2009.00435.x.
- Ralevic V. P2X receptors in the cardiovascular system and their potential as therapeutic targets in disease. Curr Med Chem 2015; 22(7): 851–865, https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867321666141215094050.
- Eklof B., Perrin M., Delis K.T., Rutherford R.B., Gloviczki P. Updated terminology of chronic venous disorders: the VEIN-TERM transatlantic interdisciplinary consensus document. J Vasc Surg 2009; 49(2): 498–501, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2008.09.014.
- Ziganshin B.A., Slavin D.A., Ziganshina A.P., Dzhordzhikiya R.K., Ziganshin A.U. Functional activity of varicose human great saphenous vein at different sites. Bull Exp Biol Med 2013; 155(4): 429–432, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-013-2169-2.
- Ziganshin A.U., Khaziakhmetov D.F., Ziganshina L.E., Khaziakhmetova V.N., Jourjikiya R.K., Ziganshin B.A., Giniyatova L.R., Burnstock G. Varicose disease affects the P2 receptor-mediated responses of human greater saphenous vein. Vascul Pharmacol 2004; 42(1): 17–21, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2004.11.007.
- Ziganshin B.A., Slavin D.A., Khaziakhmetov D.F., Ziganshina A.P., Slavin L.E., Dzhordzhikiya R.K., Ziganshin A.U. Study of the presence and localization of P2 receptors in human blood vessels. Kazanskiy meditsinskiy zhurnal 2015; 96(3): 368–376, https://doi.org/10.17750/kmj2015-368.
- Metcalfe M.J., Baker D.M., Turmaine M., Burnstock G. Alterations in purinoceptor expression in human long saphenous vein during varicose disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2007; 33(2): 239–250, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2006.12.035.
- Eklöf B., Rutherford R.B., Bergan J.J., Carpentier P.H., Gloviczki P., Kistner R.L., Meissner M.H., Moneta G.L., Myers K., Padberg F.T., Perrin M., Ruckley C.V., Smith P.C., Wakefield T.W. Revision of the CEAP classification for chronic venous disorders: consensus statement. J Vasc Surg 2004; 40(6): 1248–1252, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2004.09.027.
- Burnstock G. Noradrenaline and ATP as cotransmitters in sympathetic nerves. Neurochem Int 1990; 17(2): 357–368, https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-0186(90)90158-p.
- Burnstock G., Verkhratsky A. Evolutionary origins of the purinergic signalling system. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2009; 195(4): 415–447, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2009.01957.x.
- Burnstock G., Pelleg A. Cardiac purinergic signalling in health and disease. Purinergic Signal 2015; 11(1): 1–46, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-014-9436-1.
- Ziganshin A.U. Purine P2 receptors as potential targets for action of new drugs. Vestnik Rossiyskoi akademii meditsinskikh nauk 2011; 11: 32–38.
- Badier-Commander C., Couvelard A., Henin D., Verbeuren T., Michel J.B., Jacob M.P. Smooth muscle cell modulation and cytokine overproduction in varicose veins. An in situ study. J Pathol 2001; 193(3): 398–407, https://doi.org/10.1002/path.819.
- Ziganshin A.U., Ziganshin B.A. P2 receptors — promising targets for future drugs. Current Topics in Pharmacology 2012; 16(1): 31–43.
- Laine M., Paganelli F., Bonello L. P2Y12-ADP receptor antagonists: days of future and past. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(5): 327–332, https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i5.327.










