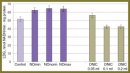
The Effect of Free and Bound Nitric Oxide on Blood Energy Metabolism
The aim of the investigation was to perform a comparative analysis of free and bound nitric oxide effects on erythrocyte energy metabolic parameters in vitro.
Materials and Methods. Two series of experiments were carried out. In the first series we processed blood samples (5 ml) by gaseous nitric oxide (800 µg/l) using three regimens of ″Plazon″ apparatus (Russia). In the second series we saturated three aliquot blood samples by 0.05; 0.1 and 0.2 ml of dinitrozyl iron complexes (DNIC) respectively (concentration of the compound was 3 mmol/l). We determined lactate dehydrogenase activity in direct and indirect reactions and lactate level in blood and erythrocytes. A number of derived coefficients were calculated to estimate energy metabolic changes.
Results. High concentrations of free nitric oxide were found to inhibit the activity of enzyme systems related to energy metabolism. On the contrary, DNIC have a stimulating effect on erythrocytes energy metabolism.
- Brune B., Lapetina E.G. Activation of cytosolic ADP-ribosyltransferase by nitric oxide-generating agents. J Biol Chem 1989; 264: 8455–8458.
- Dimmler S., Brune B. Characterization of a nitric oxide-catalysed ADP-ribosylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem 1992; 210: 305–310.
- Mohr S., Hallak H., de Boitte A., et al. Nitric oxide-induced S-glutathionylation and inactivation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 9427–9430.
- Zhang S., Snyder S.H. Nitric oxide stimulates auto-ADP-ribosylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 1992; 89: 9382–9385.
- Almeida A., Moncada S., Bolanos J.P. Nitric oxide switches on glycolysis through the AMP protein kinase and 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase pathway. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 45–51.
- Tsuura Y., Shida H., Shinomura T., et al. Endogenous nitric oxide inhibits glucose-induced insulin secretion by suppression of phosphofructokinase activity in pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998; 252: 34–38.
- Mikhaylenko V.M. Izmeneniya energeticheskogo statusa opukholevykh kletok pri deystvii ekzogennykh oksidov azota [Energy status changes of tumor cells under exogenous nitric oxides]. Sib Onkol Z — Siberian Journal of Oncology 2009; Suppl 2: 137–138.
- LeCras T.D., McMurthy I.F. Nitric oxide production in hypoxic lung. Am J Physiol 2001; 280(4): 1575–1582.
- Young M.E., Radda G.K., Leigton B. Nitric oxide stimulates glucose transport and metabolism in rat skeletal muscle in vitro. Biochem J 1997; 322: 223–228.
- Stanley W.C., Recchia F.A., Lopaschuk G.D. Myocardial substrate metabolism in the normal and failing heart. Physiol Rev 2005; 85: 1093–1120.
- Manukhina E.B., Downey H.F., Mallet R.T. Role of nitric oxide in cardiovascular adaptation to intermittent hypoxia. Exp Biol Med 2006; 231: 343–365.
- Vanin A.F. Oksid azota v biomeditsinskikh issledovaniyakh [Nitric oxide in biomedical researches]. Vestnik RAMN — Herald of RAMS 2000; 4: 3–5.
- Vanin A.F., Pisarenko O.I., Studneva I.M., et al. Deystvie dinitrozil’nogo kompleksa zheleza na metabolizm i kletochnye membrany ishemizirovannogo serdtsa krysy [The effect of dinitrozyl iron complex on metabolism and cell membranes of ischemic rat heart]. Kardiologiia — Cardiology 2009; 12: 43–49.
- Vanin A.F. Dinitrosyl iron complexes with thiolate ligands: physico-chemistry, biochemistry and physiology. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 2009; 21: 136–149.
- Chazov E.I., Rodnenkov O.V., Zorin A.V., et al. Hypotensive effect of Oxacom containing a dinitrosyl iron complex with glutathione. Animal studies and clinical trials on healthy volunteers. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 2012; 26: 148–156.
- Giliano N.Ya., Konevega L.V., Noskin L.A., et al. Dinitrosyl iron complexes with thiol-containing ligands and apoptosis: studies with HeLa cell cultures. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 2011; 24: 151–159.
- Hall C.N., Garthwaite J. What is the real physiological NO concentration in vivo? Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 2009; 12: 92–103.
- Martusevich A.K., Peretyagin S.P. Molekulyarnaya stereotipiya v realizatsii effekta nekotorykh lechebnykh fiziko-khimicheskikh faktorov: rol’ NO [Molecular stereotypy in realization of the effect of some therapeutic physicochemical factors: NO role]. Vestnik Nizhegorodskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta im. N.I. Lobachevskogo — Vestnik of Nizhny Novgorod State University named after N.I. Lobachevsky 2012; 2(Past 3): 205–210.
- Martusevich A.K., Solovyоva A.G., Peretyagin S.P., Mitrofanov V.N. Otsenka vliyaniya nekotorykh fizicheskikh faktorov na energeticheskiy metabolizm krovi in vitro [The assessment of the effect of some physical factors on blood energy metabolism in vitro]. Biomeditsina —Biomedicine 2013; 1: 103–108.
- Tatsumi T., Matoba S., Kawahara A., et al. Cytokine-induced nitric oxide production inhibits mitochondrial energy production and impairs contractile function in rat cardiac myocytes. J Am College Cardiol 2000; 35(5): 1338–1346.
- Vanin A.F., Lozinskiy V.I., Kapel’ko V.I. Polimernaya kompozitsiya dlya sozdaniya stabilizirovannoy formy dinitrozil’nogo kompleksa zheleza i metod sinteza etoy formy [Polymer compound for the development of a stable form of dinitrozyl iron complex and synthesis method of this form]. Patent RF №2291880. 2005.
- Solovyоva A.G., Zimin Yu.V. Novyy sposob otsenki dinamiki metabolizma krovi u bol'nykh s termicheskoy travmoy [A new estimation method of blood metabolism dynamics of patients with heat injuries]. Sovrem Tehnol Med — Modern Technologies in Medicine 2012; 2: 116–117.










