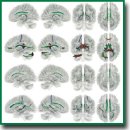
Корреляционный анализ тяжести доменов симптомов острого психоза и фракционной анизотропии трактов белого вещества головного мозга при шизофрении
Проведен анализ трактов белого вещества головного мозга (коннектомов) у пациентов с шизофренией, состояние которых определяли в парадигме дименсионального подхода.
Цель исследования — изучение связности регионов головного мозга в зависимости от тяжести клинической картины психоза при шизофрении.
Материалы и методы. 46 пациентов (22 женщины и 24 мужчины; средний возраст 26,5±5,3 года) с диагнозом шизофрении обследовали в период становления ремиссии после первого психотического эпизода. Тяжесть состояния определяли по баллам психометрических шкал PANSS, CRDPSS, BFCRS, NSA-4, FAB. Диффузионно-тензорную магнитно-резонансную томографию головного мозга выполняли с использованием 3Т МРТ Magnetom Verio (Siemens Healthineers, Германия). Расчет значимых связей между показателями обобщенной фракционной анизотропии проводящих путей мозга и тяжестью клинической картины психоза проводили на основе коэффициента ранговой корреляции Спирмена.
Результаты. Для каждого домена симптоматики были определены свои структурные особенности коннектома головного мозга, коррелирующие с тяжестью симптома. Помимо этого были визуализированы тракты, изменения в которых ассоциируются с тяжестью сразу нескольких доменов симптомов. Изменения в трактах фронтально-теменной и околообонятельной части поясного пучка правого полушария коррелируют с тяжестью проявления галлюцинаторной, негативной и кататонической симптоматики. Изменения в трактах левой фронтально-парагиппокампальной части поясного пучка отрицательно коррелируют со степенью тяжести галлюцинации и бреда, а правой фронтально-парагиппокампальной части — с тяжестью бреда и кататонии. В случаях тяжелой степени галлюцинаций, бредовых расстройств и дезорганизации наиболее значимые изменения проявляются в структурах трактов свода левого и правого полушарий. Значимые изменения в проводящих путях мозолистого тела коррелируют с выраженностью тяжести симптомов кататонии и негативной симптоматикой. Тяжесть проявления различных доменов психоза ассоциируется с различиями в структурной организации трактов головного мозга.
Заключение. Получены новые данные о возможной дифференциальной вовлеченности мозговых структур в патогенез разнообразных проявлений шизофрении, таких как галлюцинации, бред, явления дезорганизации, кататония и негативные расстройства, которые можно рассматривать в качестве объективных нейрофизиологических маркеров данного заболевания.
- Vitolo E., Tatu M.K., Pignolo C., Cauda F., Costa T., Ando’ A., Zennaro A. White matter and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging studies. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 2017; 270: 8–21, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2017.09.014.
- Honea R., Crow T.J., Passingham D., Mackay C.E. Regional deficits in brain volume in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Am J Psychiatry 2005; 162(12): 2233–2245, https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.162.12.2233.
- Podwalski P., Szczygieł K., Tyburski E., Sagan L., Misiak B., Samochowiec J. Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging in psychiatry: a narrative review of its potential role in diagnosis. Pharmacol Rep 2021; 73(1): 43–56, https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-020-00177-0.
- Demjaha A., Morgan K., Morgan C., Landau S., Dean K., Reichenberg A., Sham P., Fearon P., Hutchinson G., Jones P.B., Murray R.M., Dazzan P. Combining dimensional and categorical representation of psychosis: the way forward for DSM-V and ICD-11? Psychol Med 2009; 39(12): 1943–1955, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291709990651.
- Crow T.J. The two-syndrome concept: origins and current status. Schizophr Bull 1985; 11(3): 471–486, https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/11.3.471.
- Liddle P.F., Barnes T.R., Morris D., Haque S. Three syndromes in chronic schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 1989; 7: 119–122.
- Lindenmayer J.P., Bernstein-Hyman R., Grochowski S., Bark N. Psychopathology of schizophrenia: initial validation of a 5-factor model. Psychopathology 1995; 28(1): 22–31, https://doi.org/10.1159/000284896.
- Lehman A.F. Improving treatment for persons with schizophrenia. Psychiatr Q 1999; 70(4): 259–272, https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022082031007.
- Mucci A., Galderisi S., Amodio A., Dierks T. Neuroimaging and psychopathological domains. In: Galderisi S., DeLisi L., Borgwardt S. (editors). Neuroimaging of schizophrenia and other primary psychotic disorders. Springer, Cham; 2019; p. 57–155, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97307-4_2.
- Wheeler A.L., Voineskos A.N. A review of structural neuroimaging in schizophrenia: from connectivity to connectomics. Front Hum Neurosci 2014; 8: 653, https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00653.
- Zhang F., Daducci A., He Y., Schiavi S., Seguin C., Smith R.E., Yeh C.H., Zhao T., O’Donnell L.J. Quantitative mapping of the brain’s structural connectivity using diffusion MRI tractography: a review. Neuroimage 2022; 249: 118870, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118870.
- Kraguljac N.V., Lahti A.C. Neuroimaging as a window into the pathophysiological mechanisms of schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry 2021; 12: 613764, https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.613764.
- Chan W.Y., Yang G.L., Chia M.Y., Lau I.Y., Sitoh Y.Y., Nowinski W.L., Sim K. White matter abnormalities in first-episode schizophrenia: a combined structural MRI and DTI study. Schizophr Res 2010; 119(1-3): 52–60, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2009.12.012.
- Alderson-Day B., McCarthy-Jones S., Fernyhough C. Hearing voices in the resting brain: a review of intrinsic functional connectivity research on auditory verbal hallucinations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2015; 55: 78–87, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.04.016.
- Kubera K.M., Rashidi M., Schmitgen M.M., Barth A., Hirjak D., Sambataro F., Calhoun V.D., Wolf R.C. Structure/function interrelationships in patients with schizophrenia who have persistent auditory verbal hallucinations: a multimodal MRI study using parallel ICA. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2019; 93: 114–121, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.03.007.
- Rowland L.M., Spieker E., Holcomb H.H. A review of diffusion tensor imaging in schizophrenia. Clinical Schizophrenia & Related Psychoses 2009; 3(3): 142–154.
- Hugdahl K. Auditory hallucinations: A review of the ERC “VOICE’ project. World J Psychiatry 2015; 5(2): 193–209, https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v5.i2.193.
- Padmanabhan J.L., Tandon N., Haller C.S., Mathew I.T., Eack S.M., Clementz B.A., Pearlson G.D., Sweeney J.A., Tamminga C.A., Keshavan M.S. Correlations between brain structure and symptom dimensions of psychosis in schizophrenia, schizoaffective, and psychotic bipolar I disorders. Schizophr Bull 2015; 41(1): 154–162, https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbu075.
- McKnight R., Price J., Geddes J. Schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders. In: Psychiatry. Oxford University Press; 2019; p. 289–310, https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198754008.003.0030.
- Bopp M.H.A., Zöllner R., Jansen A., Dietsche B., Krug A., Kircher T.T.J. White matter integrity and symptom dimensions of schizophrenia: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Schizophr Res 2017; 184: 59–68, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2016.11.045.
- Thomas P., Mathur P., Gottesman I.I., Nagpal R., Nimgaonkar V.L., Deshpande S.N. Correlates of hallucinations in schizophrenia: a cross-cultural evaluation. Schizophr Res 2007; 92(1–3): 41–49, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2007.01.017.
- Jablensky A., Sartorius N., Ernberg G., Anker M., Korten A., Cooper J.E., Day R., Bertelsen A. Schizophrenia: manifestations, incidence and course in different cultures. A World Health Organization ten-country study. Psychol Med Monogr Suppl 1992; 20: 1–97. Corrected and republished from: Psychol Med Monogr Suppl 1992; 22(4): following 1092, https://doi.org/10.1017/s0264180100000904.
- Roche E., Creed L., MacMahon D., Brennan D., Clarke M. The epidemiology and associated phenomenology of formal thought disorder: a systematic review. Schizophr Bull 2015; 41(4): 951–962, https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbu129.
- Solmi M., Pigato G.G., Roiter B., Guaglianone A., Martini L., Fornaro M., Monaco F., Carvalho A.F., Stubbs B., Veronese N., Correll C.U. Prevalence of catatonia and its moderators in clinical samples: results from a meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Schizophr Bull 2018; 44(5): 1133–1150, https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbx157.
- Aandi Subramaniyam B., Muliyala K.P., Suchandra H.H., Reddi V.S.K. Diagnosing catatonia and its dimensions: cluster analysis and factor solution using the Bush Francis Catatonia Rating Scale (BFCRS). Asian J Psychiatr 2020; 52: 102002, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2020.102002.
- Sicras-Mainar A., Maurino J., Ruiz-Beato E., Navarro-Artieda R. Impact of negative symptoms on healthcare resource utilization and associated costs in adult outpatients with schizophrenia: a population-based study. BMC Psychiatry 2014; 14: 225, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-014-0225-8.
- Bobes J., Arango C., Garcia-Garcia M., Rejas J.; CLAMORS Study Collaborative Group Prevalence of negative symptoms in outpatients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders treated with antipsychotics in routine clinical practice: findings from the CLAMORS study. J Clin Psychiatry 2010; 71(3): 280–286. Corrected and republished from: J Clin Psychiatry 2011; 72(7): 1017, https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.08m04250yel.
- Yeh F.C., Verstynen T.D., Wang Y., Fernández-Miranda J.C., Tseng W.Y. Deterministic diffusion fiber tracking improved by quantitative anisotropy. PLoS One 2013; 8(11): e80713, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080713.
- Yu W., Lv Q., Zhang C., Shen Z., Sun B., Wang Z. High-angular diffusion MRI in reward-based psychiatric disorders. In: Sun B., Salles A. (editors). Neurosurgical Treatments for Psychiatric Disorders. Springer, Dordrecht; 2015, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9576-0_2.
- Yeh F.C., Badre D., Verstynen T. Connectometry: a statistical approach harnessing the analytical potential of the local connectome. Neuroimage 2016; 125: 162–171, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.053.
- Zhuo C., Fang T., Chen C., Chen M., Sun Y., Ma X., Li R., Tian H., Ping J. Brain imaging features in schizophrenia with co-occurring auditory verbal hallucinations and depressive symptoms — implication for novel therapeutic strategies to alleviate the reciprocal deterioration. Brain Behav 2021; 11(2): e01991, https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1991.
- Martí-Bonmatí L., Lull J.J., García-Martí G., Aguilar E.J., Moratal-Pérez D., Poyatos C., Robles M., Sanjuán J. Chronic auditory hallucinations in schizophrenic patients: MR analysis of the coincidence between functional and morphologic abnormalities. Radiology 2007; 244(2): 549–556, https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2442060727.
- Hubl D., Koenig T., Strik W., Federspiel A., Kreis R., Boesch C., Maier S.E., Schroth G., Lovblad K., Dierks T. Pathways that make voices: white matter changes in auditory hallucinations. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004; 61(7): 658–668, https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.61.7.658
- Rădulescu A.R., Mujica-Parodi L.R. A systems approach to prefrontal-limbic dysregulation in schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 2008; 57(4): 206–216, https://doi.org/10.1159/000151731.
- Abdul-Rahman M.F., Qiu A., Woon P.S., Kuswanto C., Collinson S.L., Sim K. Arcuate fasciculus abnormalities and their relationship with psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia. PLoS One 2012; 7(1): e29315, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029315.
- Fitzsimmons J., Schneiderman J.S., Whitford T.J., Swisher T., Niznikiewicz M.A., Pelavin P.E., Terry D.P., Mesholam-Gately R.I., Seidman L.J., Goldstein J.M., Kubicki M. Cingulum bundle diffusivity and delusions of reference in first episode and chronic schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 2014; 224(2): 124–132, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2014.08.002.
- Whitford T.J., Kubicki M., Pelavin P.E., Lucia D., Schneiderman J.S., Pantelis C., McCarley R.W., Shenton M.E. Cingulum bundle integrity associated with delusions of control in schizophrenia: preliminary evidence from diffusion-tensor tractography. Schizophr Res 2015; 161(1): 36–41, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2014.08.033.
- Braun U., Schaefer A., Betzel R.F., Tost H., Meyer-Lindenberg A., Bassett D.S. From maps to multi-dimensional network mechanisms of mental disorders. Neuron 2018; 97(1): 14–31, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.007.
- Harvey P.D., Strassnig M. Predicting the severity of everyday functional disability in people with schizophrenia: cognitive deficits, functional capacity, symptoms, and health status. World Psychiatry 2012; 11(2): 73–79, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wpsyc.2012.05.004.
- Galderisi S., Rossi A., Rocca P., Bertolino A., Mucci A., Bucci P., Rucci P., Gibertoni D., Aguglia E., Amore M., Bellomo A., Biondi M., Brugnoli R., Dell’Osso L., De Ronchi D., Di Emidio G., Di Giannantonio M., Fagiolini A., Marchesi C., Monteleone P., Oldani L., Pinna F., Roncone R., Sacchetti E., Santonastaso P., Siracusano A., Vita A., Zeppegno P., Maj M; Italian Network For Research on Psychoses. The influence of illness-related variables, personal resources and context-related factors on real-life functioning of people with schizophrenia. World Psychiatry 2014; 13(3): 275–287, https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20167.
- Galderisi S., Mucci A., Buchanan R.W., Arango C. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia: new developments and unanswered research questions. Lancet Psychiatry 2018; 5(8): 664–677, https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30050-6.
- de Wit S., Watson P., Harsay H.A., Cohen M.X., van de Vijver I., Ridderinkhof K.R. Corticostriatal connectivity underlies individual differences in the balance between habitual and goal-directed action control. J Neurosci 2012; 32(35): 12066–12075, https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1088-12.2012.
- Gansler D.A., McLaughlin N.C., Iguchi L., Jerram M., Moore D.W., Bhadelia R., Fulwiler C. A multivariate approach to aggression and the orbital frontal cortex in psychiatric patients. Psychiatry Res 2009; 171(3): 145–154, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2008.03.007.
- Hirjak D., Rashidi M., Kubera K.M., Northoff G., Fritze S., Schmitgen M.M., Sambataro F., Calhoun V.D., Wolf R.C. Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging data fusion reveals distinct patterns of abnormal brain structure and function in catatonia. Schizophr Bull 2020; 46(1): 202–210, https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbz042.
- Palomero-Gallagher N., Hoffstaedter F., Mohlberg H., Eickhoff S.B., Amunts K., Zilles K. Human pregenual anterior cingulate cortex: structural, functional, and connectional heterogeneity. Cereb Cortex 2019; 29(6): 2552–2574, https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy124.
- Bubb E.J., Metzler-Baddeley C., Aggleton J.P. The cingulum bundle: anatomy, function, and dysfunction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2018; 92: 104–127, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.05.008.
- Benear S.L., Ngo C.T., Olson I.R. Dissecting the fornix in basic memory processes and neuropsychiatric disease: a review. Brain Connect 2020; 10(7): 331–354, https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2020.0749.
- Efimova O., Pavlov K., Kachanovskiy M., Ayupova A., Zorkina Ya., Morozova A., Andreyuk D., Kostyuk G. Gene expression asymmetry in the human prefrontal cortex. In: Velichkovsky B.M., Balaban P.M., Ushakov V.L. (editors). Advances in cognitive research, artificial intelligence and neuroinformatics. Intercognsci 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1358. Springer, Cham; 2021; p. 464–472, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71637-0_53.
- Gutiérrez-Fernández J., Luna Del Castillo Jde D., Mañanes-González S., Carrillo-Ávila J.A., Gutiérrez B., Cervilla J.A., Sorlózano-Puerto A. Different presence of Chlamydia pneumoniae, herpes simplex virus type 1, human herpes virus 6, and Toxoplasma gondii in schizophrenia: meta-analysis and analytical study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2015; 11: 843–852, https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S79285.
- Gogtay N., Giedd J.N., Lusk L., Hayashi K.M., Greenstein D., Vaituzis A.C., Nugent T.F. 3rd, Herman D.H., Clasen L.S., Toga A.W., Rapoport J.L., Thompson P.M. Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004; 101(21): 8174–8179, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0402680101.
- Шмуклер А.Б. Структурно-функциональная рассогласованность различных отделов головного мозга при шизофрении: роль интегративной перцепции. Социальная и клиническая психиатрия 2010; 20(3): 86–95.
- Mosina L., Ushakov V., Orlov V., Kartashov S., Zakharova N., Kostyuk G. Assessment and correlation of morphometric and tractographic measures of patients diagnosed with schizophrenia. In: Samsonovich A.V., Liu T. (editors). Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures 2023. BICA 2023. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1130. Springer, Cham; 2024; p. 612–626, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50381-8_65.










